Since the switchover to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) in 2023, team after team has approached us with questions, concerns, and overall confusion about the platform.
In most cases, account configuration is to blame, with improper tracking and missing data being the most common errors. As a result, those who relied on Google’s automatic GA4 migration are left scrambling to recover crucial data needed to inform their business and marketing decisions.
If you’re in the same boat, you’ve come to the right place.
Here at Inflow, we offer an extensive Google Analytics 4 audit to find (and resolve) common errors. Conducted by our team of GA4-certified experts, this audit helps set our clients on the right path with clean and complete data moving forward.
But, in response to the overwhelming demand for GA4 resources, we’ve also created this quick-fix guide to fill the gaps.
Below, find a sneak peek of our step-by-step process for conducting a GA4 audit, including some of the most common errors we’ve identified in client accounts over the last few years.
For the full version of this audit, completed by our in-house experts, contact our team now.
What is a Google Analytics Audit?
A Google Analytics audit reviews your implementation and usage of GA4 to ensure it is set up correctly and you’re using it effectively to make data-driven decisions.
An audit will identify areas where you can improve your tracking or analysis to get more out of the platform. For example, you might find that you’re not tracking important eCommerce metrics or that your reports could be more user-friendly.
We recommended you audit your Google Analytics accounts regularly for ongoing site health, but especially:
- Before launching a website: Ensure your tracking is set up correctly from the outset to avoid losing any data.
- After making major changes to your website: If you have made significant changes (such as a redesign or content overhaul), an audit will guarantee that your tracking has been updated accordingly and all data is still being collected correctly.
- During a website migration: If you’re moving your website to a new platform, you need to ensure your tracking is set up correctly on the new site, so you don’t lose any data.
- When adding or changing KPIs: If your business goals or ways to measure them are changing (for example, you’re seeing increased phone calls from your website) then you want to make sure your GA4 is set up to track and report on those efforts.
Google Analytics 4 Audit Checklist
Below, we’ve listed a few key elements of our comprehensive Google Analytics audit checklist. Use them to evaluate your current account configuration and data tracking, identify errors, and create a plan for GA4 optimization.
Note: Before you start auditing your Google Analytics 4 accounts, make sure you understand how the platform differs from Universal Analytics. Due to the difference in the underlying data models, you can’t configure your GA4 accounts identically to your UA accounts. Certain metrics will report inconsistencies because of the way they’re tracked; this isn’t a mistake but a feature of the platform itself.
We recommend reviewing the following guides to get caught up:
- Google Analytics 4 vs. Universal Analytics: Data & Reporting
- Google Analytics 4 vs. Universal Analytics: Data & Reporting
- Why Your Google Analytics 4 Data Doesn’t Match Up
Remember that GA4 has come a long way since its launch in 2020. Many features have been added or changed; make sure to review them in detail so you can get the most out of your GA4.
Now, let’s get started.
(You can also download a PDF version of this GA4 audit checklist at the bottom of this blog.)
1. Are your pages tagged using the proper analytics code?
First and foremost, every page on your website must be tagged with the appropriate analytics code to report accurate, real-time data. This can be done via Google Tag Manager (GTM) or through gtag.js — but not both, as this can lead to double event counting in Google Analytics 4.
At Inflow, we recommend using the former to implement your tracking code. GTM allows you to manage website tags (such as analytics and marketing pixels) in one place. It also enables adding, removing, or editing tags without touching the code of each page.
To review your tag configuration:
- Go to “Tags > New > Tag Configuration.”
- Select “Google Analytics.”
- Select “Google Tag” or “Google Analytics: GA4 Event” and fill out the information.
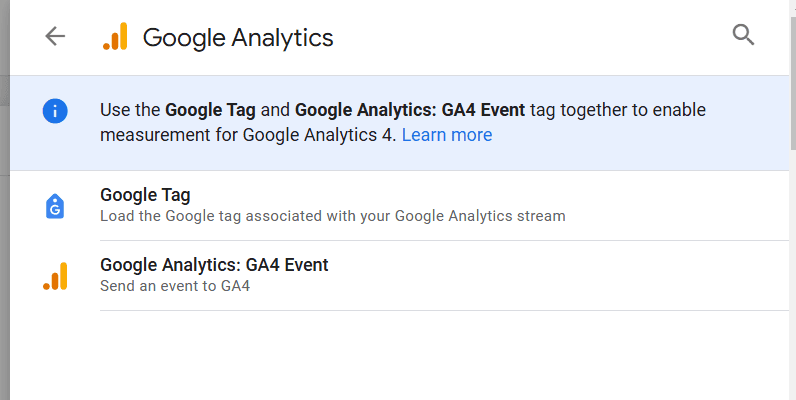
To further customize configuration or event tags, check out Google’s guide.
You can use a tool like Google’s Tag Assistant to help verify your sitewide tags and identify any duplicate tracking mistakenly set up by your development team.
Alternatively, we offer a Google Tag Manager audit to review your configuration and streamline your website tracking strategy. Contact us today to learn more.
2. Do you have Enhanced Measurements turned on?
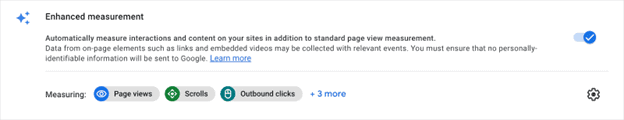
To take full advantage of GA4’s capabilities, your account needs to have Enhanced Measurements turned on. This will allow for features like automatic event detection for actions like page views, scrolls, video views, and link clicks.
To review your Enhanced Measurements settings:
- In the “Property” column, select “Data Streams > Web.”
- Slide the Enhanced measurement switch to “On.” (You can edit individual event options with the gear icon.)
3. Do you have the proper number of data streams enabled?
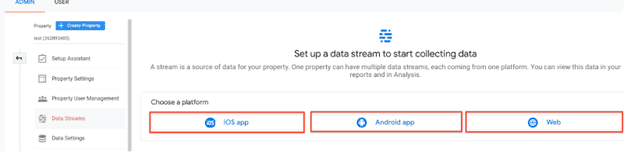
Each Google Analytics 4 property can have up to 50 data streams (flow of data from a customer touchpoint to Analytics). Most companies only need one data stream to account for their single website. If your business has an app, you’ll need a separate data stream to feed that customer information into GA4.
To review your data streams, select “Data Streams” under the “Property” dropdown in the Admin section.
4. Have you changed your data retention period?
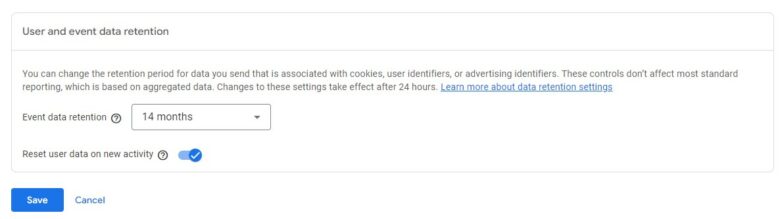
By default, all Google Analytics 4 properties are set to retain data for two months. However, the platform allows for a retention period of up to 14 months on free accounts, which will provide the best data comparison within the GA4 reporting platform.
(Note: Google Analytics 360 allows for up to 50 months of data retention as part of its paid subscription model.)
To change your data retention period, go to “Data Settings > Data Retention” under the Admin section.
5. Have you linked necessary third-party platforms?
For the fullest picture of your Google Analytics data, make sure that you’ve connected third-party platforms, including Google Search Console, Google Ads (formerly known as Adwords), and BigQuery. Without these links, you’ll be missing out on key attribution and performance data from your marketing campaigns.
To link appropriate platforms, navigate to the “Product Links” section in Admin. There, you’ll be able to connect third-party apps and feed appropriate data to your GA4 property.
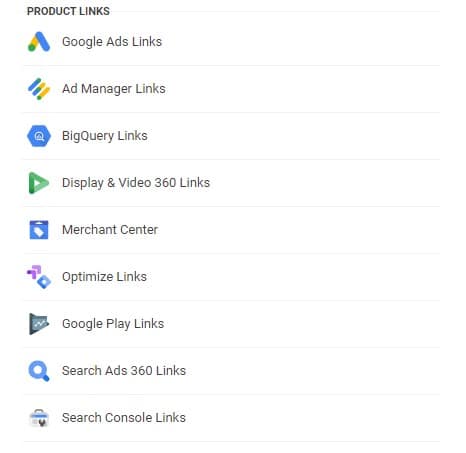
As a reminder, because of data retention limitations in GA4, you’ll want a third-party data streaming warehouse to store data. We’ve been using BigQuery for our clients; it’s an affordable and valuable option for most mid-sized businesses.
6. Did you remember to configure cross-domain tagging?
Cross-domain tagging and proper link tagging are required to collect data from other websites. Otherwise, you risk losing data as users go from one site to another. You can easily set up cross-domain tagging in the GA4 user interface by following the video below.
The video below is hosted on YouTube. If you need assistance with viewing the video, please contact info@goinflow.com.
You should also keep an eye out for the following red flags:
- Other domains tracking traffic to your GA4 profile after mistakenly scraping your GA tracking code
- Traffic from test or development servers, which often use the same GA snippet as your live site
7. Are you tracking unnecessary URLs with messy parameters?
This is probably the most important, most overlooked, and trickiest part of a GA4 audit.
Universal Analytics made it easy to filter out unnecessary URLs in internal reports, but it’s a little more complicated in Google Analytics 4. For that reason, we frequently review analytics reports where traffic for a single web page is “split” in GA4 among multiple URLs with unwanted UTM parameters, making the resulting numbers hard to analyze.
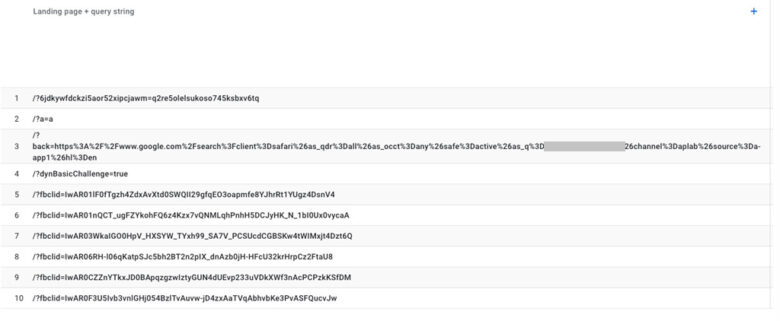
We also often find URL parameters being used for sorting content, such as filtered category pages.
To resolve this, eliminate duplicate URLs by stripping out unwanted parameters in GTM and only using the default URL.
However, make sure to discuss with your marketing team before eliminating specific parameters. While some will be unnecessary for your business needs, others may hold value for your internal reporting.
Similarly, if you’re only seeing a few extra URLs with parameters, it may not make a difference in your bottom-line reporting. When in doubt, talk with your marketing and analytics team to identify the best plan of action.
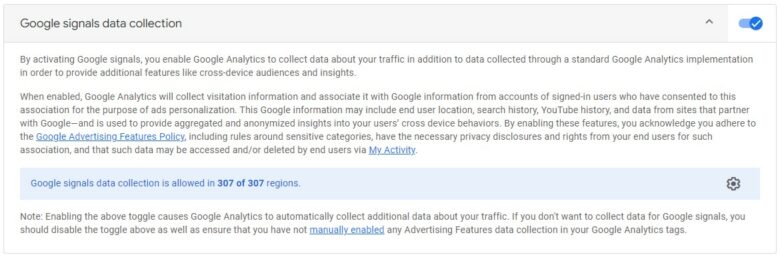
8. Did you activate Google Signals?
Google Signals refers to session data from sites and applications connected with Google account users. This combination of data and signed-in users delivers cross-device reporting, remarketing, and the like.
The video below is hosted on YouTube. If you need assistance with viewing the video, please contact info@goinflow.com.
While there are valid reasons for turning Google Signals off (often related to data privacy laws within your country), it’s a decision that you’ll need to make internally. When used purposefully, Google Signals can enhance your data collection and reporting capabilities — but they do come with legal considerations.
You can turn on your Google Signals within the Property column of your account. Under “Data Settings > Data Collection,” you can toggle on/off the “Google signals data collection” button. (Note: You must be designated as an “Editor” in your Google Analytics 4 property settings to use Google Signals.)
9. Have you turned on site search tracking?
If your website has a search feature, you should be tracking it.
Site search tracking can provide key insights into what people are looking for on your site and how well it’s meeting those needs. Internal site search data can inform many aspects of your strategy, especially your SEO efforts.
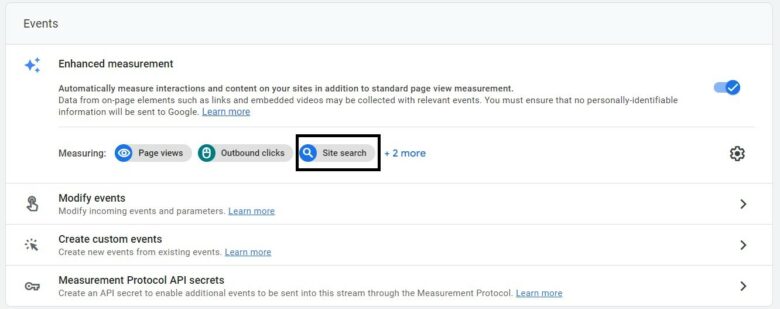
To set up site search tracking in GA4:
- Select “Data Streams” under the “Property” column.
- You will now see all available streams. Select the stream on which you want to set up search site tracking.
- Under “Enhanced Measurement,” select the gear icon.
- Ensure that the Site Search option is enabled.
Note: If your site search parameters aren’t among those automatically tracked by Google, there will be a few additional steps to follow. Read more about that here. (You may also need to set up a custom dimension to track your search terms.)
10. Have you properly set up event tracking?
While Google Analytics 4 automatically tracks certain events within the platform, we’ve found that, more often than not, many businesses are missing the specific event tracking needed to report on their KPIs and goals. These include events like form submissions, newsletter signups, etc.
As you review the existing events in your GA4, bring your marketing and sales teams into the loops. Decide which micro- and macro-events are needed for your reporting and strategy-building; you’ll most likely need to manually add those into GA4 to measure them.
You’ll also need to set any custom dimensions or metrics needed for each event.
You can review and add events under the “Events” tab in the Admin section of GA4.
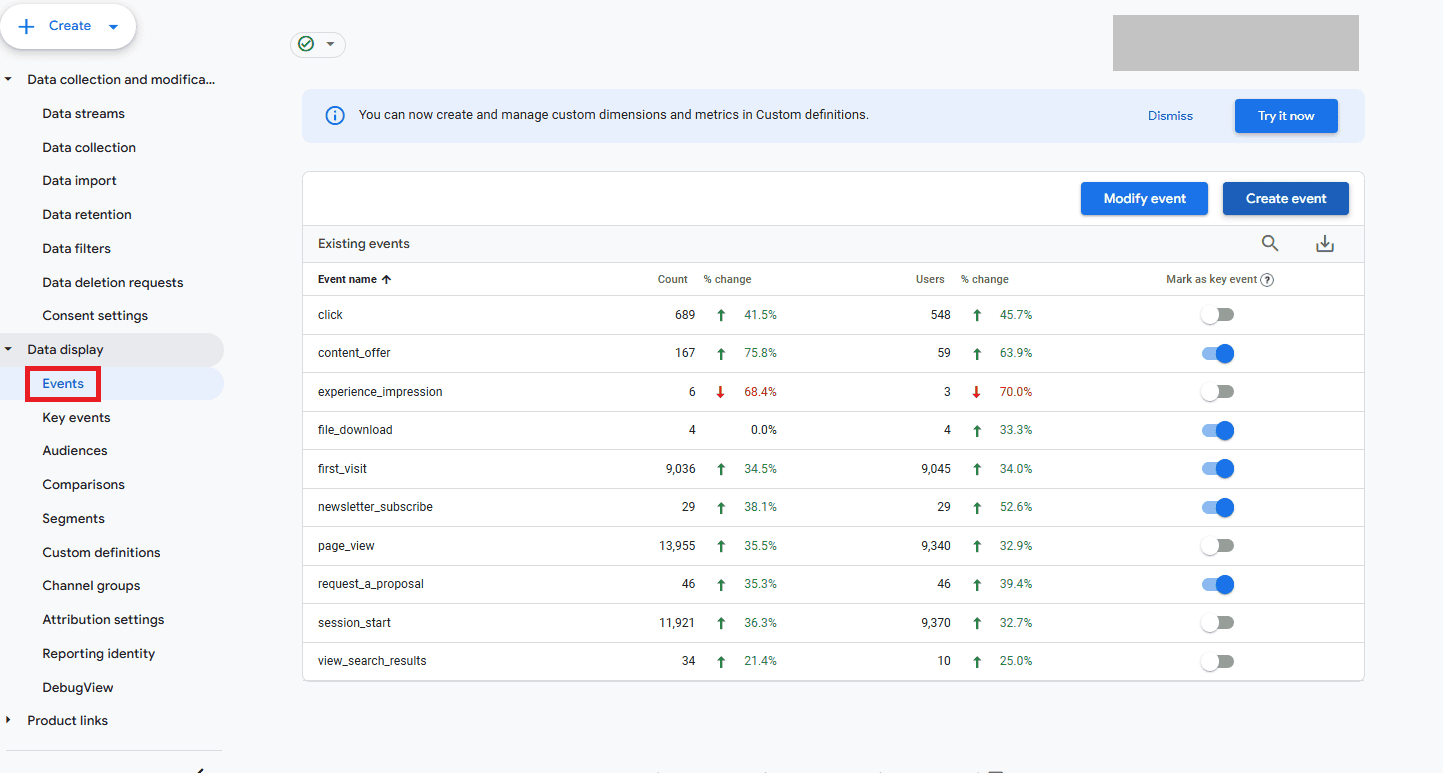
If you want to monetize any events, you’ll need to modify event conditions and parameters. (You can learn to do that here.)
eCommerce Events
eCommerce tracking provides an additional level of data above and beyond simple goal tracking. If you manage an eCommerce website, don’t overlook this important step.
Your Google Analytics 4 may already be set up to track certain eCommerce events like purchase. But, for a complete picture of your sales funnel, you’ll want to add events like “add_to_cart” and “view_item.”
Adding these events will help you flesh out your eCommerce funnel reporting.
The video below is hosted on YouTube. If you need assistance with viewing the video, please contact info@goinflow.com.
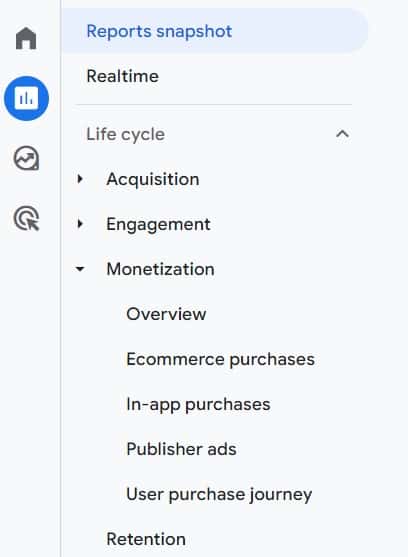
To view eCommerce data in your GA4:
- In the reporting menu, click “Monetization.”
- Click on “Overview.”
- You will see details such as Total Purchasers, Total Revenue, and Average Purchase Revenue Per Active User.
- Click “eCommerce Purchases” in the reporting menu to get a more detailed report, such as purchases by name over time, item purchase quantity, etc.
Setting up eCommerce events will require adding code for each event to your webside, so it’s best to have your developer handle it.
For more information, check out this guide from Google.
The video below is hosted on YouTube. If you need assistance with viewing the video, please contact info@goinflow.com.
11. Are any filters or modifications affecting your reporting?
Finally, check to see whether any other filters or modifications are affecting your analytics.
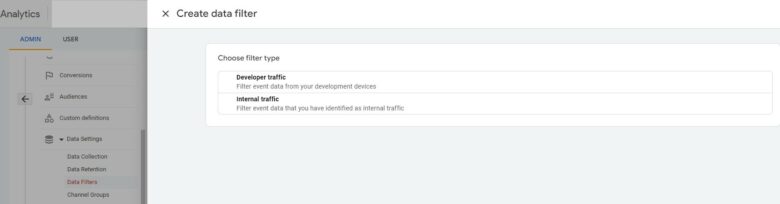
In Google Analytics 4, report filters are different than data filters. While GA4 can Filter Internal IP Traffic and Exclude Unwanted Referral Traffic, it cannot set up additional filters for data transformation or inclusions/exclusions. Compare this to UA, where you could create views that excluded certain data (such as internal traffic).
With GA4, you’ll have to create separate properties or use BigQuery. You can, however, use data filters to apply new filters on GA4 reports.
To review and set up default filters in Google Analytics 4, you must first add the IPs as Internal under the “Define internal traffic” setting. From there you will need to navigate to the “Data Settings > Data Filters” in the Admin section. There you’ll find the internal data filter you created.
Get a Full Google Analytics 4 Audit from Inflow Today
Remember, performing regular Google Analytics audits ensures you’re staying on top of your website data and taking full advantage of your investment in GA4.
Of course, to do that, you need to make sure your current Google Analytics setup is as complete as it can be.
While the checklist in this guide is a great place to start, it’s nowhere near the level of complexity and detail that’s required to maximize your Google Analytics 4 experience. We highly recommend working with a qualified team of professionals (like those at Inflow) to conduct a thorough audit of every aspect of your account.
Only that way can you ensure you’ve got the data you need to make smart business decisions.
We offer a comprehensive Google Analytics 4 audit, complete with a 50-point deliverable of recommendations and a personalized follow-up call with our certified experts. (And, if you choose to sign up for recurring digital marketing services, we’ll throw in your audit for free as part of your onboarding process.)
Get started now by filling out our form below:
Request Your
Google Analytics 4 Audit Now
In the meantime, use the following downloadable GA4 audit template as a starting point and familiarize yourself with our other guides to make the most of your analytics tools.











0 Comments